Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Testing for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (often abbreviated HWE) is a fairly common practice in population genetics. In a two-allele system, the HWE equation is defined as: , where is the frequency of the first allele and is the frequency of the second allele. The formula describes the frequency of all possible genotypes where
| HWE variable | Genotype | State |
|---|---|---|
| "pp" | homozygous | |
| "qq" | homozygous | |
| "pq" | heterozygous |
Testing for deviation from HWE is usually done with a Chi-Squared () test, where one compares the observed genotype frequencies to the expected genotype frequencies given the observed allele frequencies at a locus. Specifically, the equation is
where is the observed genotype frequency and is the expected genotype frequency for a locus. To generate our test statistic, we calculate the degrees of freedom:
and use this as the parameter for our distribution, followed by a cumulative density function using this distribution and our value calculated above.
Chi-Squared Test
hwetest(data::PopData, by::String = "locus", correction::String = "none")
Calculate chi-squared test of HWE for each locus and returns observed and expected heterozygosity with chi-squared, degrees of freedom and p-values for each locus. Use by = "population" to perform this separately for each population (default: "locus"). Use correction = to specify a P-value correction method for multiple testing (recommended). For convenience, the correction method is appended to the name of the column, so you will always know how those P-values were adjusted.
Arguments
data: the inputPopData
Keyword arguments
by:"locus"(default) or"population"correction: a string specifying a P-value adjustment type (default: "none")
correction methods
"bonferroni": Bonferroni adjustment"holm": Holm adjustment"hochberg": Hochberg adjustment"bh": Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment"by": Benjamini-Yekutieli adjustment"bl": Benjamini-Liu adjustment"hommel": Hommel adjustment"sidak": Šidák adjustment"forwardstop"or"fs": Forward-Stop adjustment"bc": Barber-Candès adjustment
🤔 For more information on multiple testing adjustments, see MultipleTesting.jl
Examples
- HWE Chi-Sq
- HWE with P adjustment
- HWE by population
julia> hwetest(@gulfsharks)
2209×4 DataFrame
Row │ locus chisq df P
│ String Float64 Int64 Float64
──────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ contig_35208 94.5678 6 0.0
2 │ contig_23109 50.789 2 9.36085e-12
3 │ contig_4493 40.7903 2 1.38832e-9
4 │ contig_10742 14.7325 2 0.000632247
5 │ contig_14898 58.1948 2 2.30704e-13
6 │ contig_8483 4.05732 2 0.131511
7 │ contig_8065 18.0799 2 0.000118574
8 │ contig_14708 13.6264 2 0.00109919
⋮ │ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
2203 │ contig_18959 106.658 2 0.0
2204 │ contig_43517 23.8965 2 6.47041e-6
2205 │ contig_27356 14.4493 2 0.000728417
2206 │ contig_475 76.6038 2 0.0
2207 │ contig_19384 13.7915 2 0.00101209
2208 │ contig_22368 20.3787 2 3.75686e-5
2209 │ contig_2784 6.13433 2 0.0465531
2194 rows omitted
julia> hwetest(@gulfsharks, correction = "bh")
2209×5 DataFrame
Row │ locus chisq df P P_bh
│ String Float64 Int64 Float64 Float64
──────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ contig_35208 94.5678 6 0.0 0.0
2 │ contig_23109 50.789 2 9.36085e-12 2.85215e-11
3 │ contig_4493 40.7903 2 1.38832e-9 3.62505e-9
4 │ contig_10742 14.7325 2 0.000632247 0.00102164
5 │ contig_14898 58.1948 2 2.30704e-13 7.91345e-13
6 │ contig_8483 4.05732 2 0.131511 0.143532
7 │ contig_8065 18.0799 2 0.000118574 0.000204314
8 │ contig_14708 13.6264 2 0.00109919 0.00170656
⋮ │ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
2203 │ contig_18959 106.658 2 0.0 0.0
2204 │ contig_43517 23.8965 2 6.47041e-6 1.27163e-5
2205 │ contig_27356 14.4493 2 0.000728417 0.00116769
2206 │ contig_475 76.6038 2 0.0 0.0
2207 │ contig_19384 13.7915 2 0.00101209 0.00160958
2208 │ contig_22368 20.3787 2 3.75686e-5 6.82475e-5
2209 │ contig_2784 6.13433 2 0.0465531 0.0561375
2194 rows omitted
julia> hwetest(@gulfsharks, by = "population")
15463×5 DataFrame
Row │ locus population chisq df P
│ String String Float64 Int64 Float64?
───────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ contig_35208 CapeCanaveral 6.47676 2 0.0392275
2 │ contig_35208 Georgia 15.7481 2 0.000380481
3 │ contig_35208 SouthCarolina 14.2857 2 0.00079049
4 │ contig_35208 FloridaKeys 27.1399 6 0.000136324
5 │ contig_35208 MideastGulf 16.6453 2 0.000242956
6 │ contig_35208 NortheastGulf 10.7263 6 0.0972136
7 │ contig_35208 SoutheastGulf 8.62222 2 0.0134186
8 │ contig_23109 CapeCanaveral 6.19376 2 0.0451901
⋮ │ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
15457 │ contig_2784 CapeCanaveral 0.0 0 missing
15458 │ contig_2784 Georgia 0.0 0 missing
15459 │ contig_2784 SouthCarolina 0.0 0 missing
15460 │ contig_2784 FloridaKeys 3.11065 2 0.211121
15461 │ contig_2784 MideastGulf 2.11686 2 0.346999
15462 │ contig_2784 NortheastGulf 0.0 0 missing
15463 │ contig_2784 SoutheastGulf 1.04091 2 0.594251
15448 rows omitted
When doing this test by population, you may notice some loci have missing P-values for certain populations, indicating that this locus is missing for that population.
Interpreting the results
Since the results are in table form, you can easily process the table using DataFramesMeta.jl or Query.jl to find loci above or below the alpha threshold you want. As an example, let's perform an HWE-test on the nancycats data without any P-value adjustments:
julia> ncats_hwe = hwetest(@nancycats , by = "population") ;
Now, we can now filter this table and leave only what we're interested in:
julia> ncats_hwe[(ncats_hwe.P .!== missing) .& (ncats_hwe.P .<= 0.05), :]
With this command, we filter the table for:
- the P-values are not
missing - the P-values are less than or equal to 0.05.
Note: You can use DataFramesMeta.jl, Query.jl, SplitApplyCombine.jl and others for more declarative dataframe manipulation.
This results in a table that now only includes non-missing P-values of 0.05 or lower:
71×5 DataFrame
Row │ locus population chisq df P
│ String String Float64 Int64 Float64?
─────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ fca8 2 74.3426 30 1.24317e-5
2 │ fca8 3 85.2 42 9.15914e-5
3 │ fca8 6 70.4136 42 0.00390639
4 │ fca8 7 63.3673 30 0.00035342
5 │ fca8 10 26.4489 12 0.00926812
6 │ fca8 11 60.801 42 0.0302593
7 │ fca8 16 26.15 12 0.0102213
8 │ fca8 17 57.2 30 0.00198256
⋮ │ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮
65 │ fca96 16 37.0033 20 0.0116913
66 │ fca37 1 12.6562 6 0.0488314
67 │ fca37 3 24.1481 12 0.0194174
68 │ fca37 5 61.1317 12 1.40268e-8
69 │ fca37 7 13.0062 6 0.042938
70 │ fca37 11 61.8056 42 0.024858
71 │ fca37 12 61.618 42 0.0257958
56 rows omitted
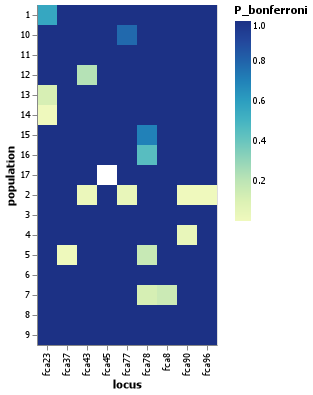
Visualizing the results
While not strictly necessary, it might sometimes make sense to generate of heatmap of the results for easier visualization. This is feasible for the nancycats data, but when loci are in the hundreds or thousands, this method quickly becomes counterproductive. In any case, here is a simple example of the HWE results for nancycats plotted as a heatmap using VegaLite.jl (other packages like Makie.jl, Plots.jl, Gadfly.jl etc. would work great too!):
using VegaLite
julia> ncats_hwe = hwetest(@nancycats , by = "population", correction = "bonferroni");
julia> ncats_hwe |> @vlplot(:rect, :locus, :population, color=:P_bonferroni)
Acknowledgements
While most of the arithmetic for the Hardy-Weinberg test is written by us, we rely on the Chi-Squared distribution and probability density function provided by Distributions.jl.